This article emphasizes the need to generate energy savings through energy efficiency projects. This need is not only based on the inherently positive nature of savings but also on the obligations established by the EU in Directive 2012/27/EU of the European Parliament and the Council, dated October 25, 2012, regarding energy efficiency. The Energy Savings Certificates (ESC System or CAE System in Spain) emerge to facilitate investment in energy efficiency technologies and foster a market in this sector.
Therefore, given the obligation of obligated parties to contribute to the National Energy Efficiency Fund (FNEE), a new market is created where companies can purchase the necessary savings from companies that carry out projects generating these savings. These energy savings are obtained as certificates and verified by an independent organisation. Alternatively, obligated parties can purchase Energy Savings Certificates (CAE in Spain) from other obligated parties and delegated parties to voluntarily fulfil part of their financial obligation.
Order TED/815/2023, dated July 18, establishes the ESC System, which partially develops Royal Decree 36/2023 issued on January 24, regarding the Energy Savings Certificates System (RD 36/2023) in Spain. It is carried out following the provisions of Law 18/2014, dated October 15, approving urgent measures for growth, competitiveness, and efficiency.
Agents involved in the ESC System in Spain
- Obligated Parties: Gas and electricity trading companies, wholesale operators of petroleum products and liquefied petroleum gases, as established in Article 69 of Law 18/2014, dated October 15.
- Delegated Parties: Public or private entities that can assume, either fully or partially, the delegation for obtaining energy savings from one or more obligated parties. They need to be accredited beforehand by the National Coordinator of the ESC System.
- Savings Owner: Individuals or legal entities, public or private, that invest in energy efficiency to achieve energy savings for themselves or third parties. This category also includes recipients of the savings generated by such investments.
- Energy Savings Verifier: Entity accredited by the National Accreditation Body (ENAC). They can be chosen freely by obligated or delegated parties and are responsible for verifying the energy savings achieved through energy efficiency actions. They also verify that the documentation submitted in the ESC dossier meets all information requirements.
- Regional Manager: Responsible for validating the information collected in the ESC dossier.
- National Coordinator of the ESC System: Responsible for ensuring its proper functioning.
Obtaining an ESC in Spain
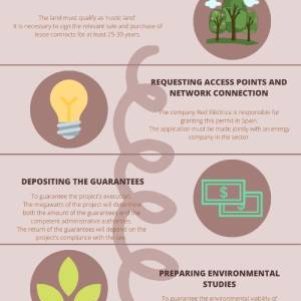
Energy efficiency improvements carried out from January 26, 2023, onwards that comply with the requirements outlined in Directive 2012/27/EU and other applicable regulations may be eligible for ESC.
Only obligated parties and delegated parties can request the issuance of ESC after obtaining a favourable verification report from an energy savings verifier for the following types of actions:
- Specific Actions: These are energy efficiency measures with unique technical characteristics not covered in the standardized catalogue.
- Standardized Actions: These are energy efficiency measures with technical characteristics that allow easy replication.
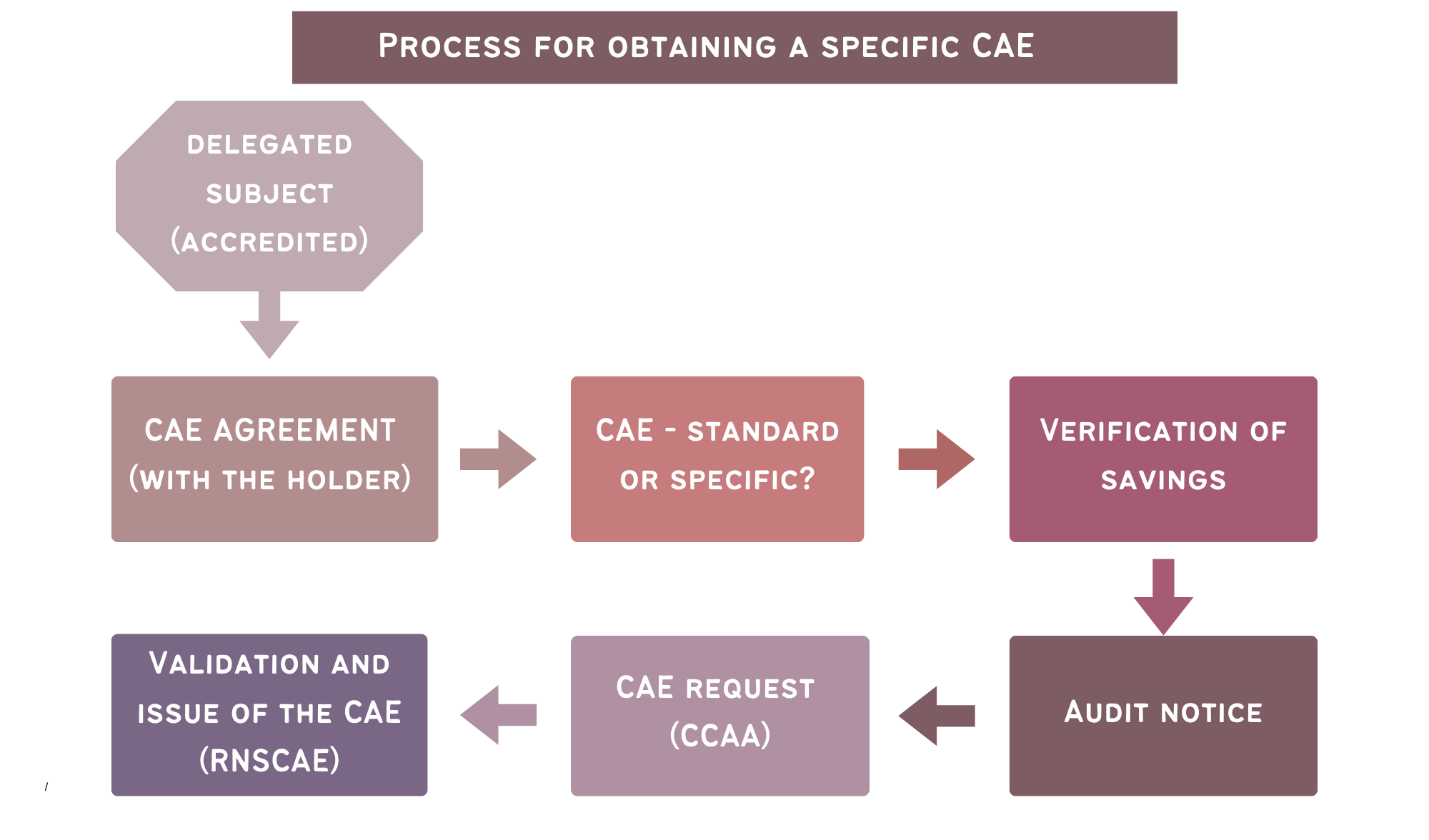
The application for ESC issuance will be submitted through the ESC System’s electronic platform for review and analysis by the Regional Manager. If approved, the corresponding ESC will be issued. Once issued, the National Coordinator of the ESC System will register them in the National Registry. Subsequently, they can be traded or settled in the name of the obligated party or on behalf of the delegated party, as applicable.
In any case, the energy savings certificates (ESC) is a complex process requiring specialised guidance, which will be essential for achieving the objectives smoothly.
If you need additional information regarding the energy savings certificates (CAE or ESC) in Spain,